Bitumen, a complex and resilient substance derived from the distillation of crude oil, occupies a prominent position within various industries due to its diverse array of applications. Often recognized for its role in road construction, bitumen serves as the binding agent that forms the durable asphalt surfaces found on highways and streets worldwide.
As a highly viscous and dense petroleum product, bitumen exhibits a distinct set of characteristics that set it apart from other oil derivatives. Its composition consists of hydrocarbons that are considerably heavier than those present in lighter petroleum products. This unique molecular makeup grants bitumen its remarkable durability and resistance to the elements, making it an exceptional choice for creating roadways that can withstand heavy traffic loads, extreme weather conditions, and the wear and tear of time.
Beyond its role in infrastructure, bitumen finds utility in various industrial applications. It serves as a vital component in the manufacturing of roofing materials, providing protection against water infiltration and contributing to the longevity of buildings. Additionally, bitumen has been employed in waterproofing applications, ensuring the integrity of structures such as reservoirs and underground storage facilities.
The versatile nature of bitumen is further underscored by its presence in the realm of art and craftsmanship. Historically used as an adhesive and sealant, bitumen has also been incorporated into art mediums, offering artists an unconventional and intriguing tool for their creative expressions.
In essence, bitumen’s multifaceted attributes extend far beyond its conventional role in road construction. Its resilience, versatility, and enduring properties make it an essential resource that bridges the realms of infrastructure, industry, and art, showcasing its significance in shaping the modern world.
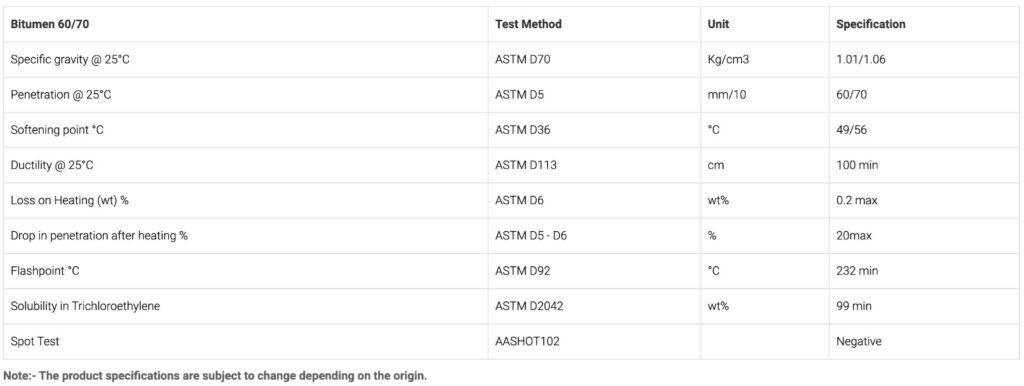
Product Specifications